Alfa Laval and its exchangers against the energetic crisis
Alfa Laval heat exchangers will help to deal with the global energy crisis Alfa Laval heat exchangers focus on reducing carbon dioxide emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions. Moreover, the exchangers provide high efficiency even in difficult operating conditions, maintaining a high number of heat exchange units. To have a better idea about Alfa Laval’s commitment […]

Alfa Laval heat exchangers will help to deal with the global energy crisis
Alfa Laval heat exchangers focus on reducing carbon dioxide emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions. Moreover, the exchangers provide high efficiency even in difficult operating conditions, maintaining a high number of heat exchange units.
To have a better idea about Alfa Laval’s commitment we can start from Taiyuan. A city located in a region of north-eastern China, called the “city of smog” due to its high levels of air pollution. In 2014 the Chinese government started to fight pollution by adopting stricter measures against polluting companies. Millions of tons of CO2 emissions and thousands of tons of noxious dust, sulfur dioxide and oxychlorides will soon be drastically lower thanks to the opening of a new power plant and to Alfa Laval technology contribution.
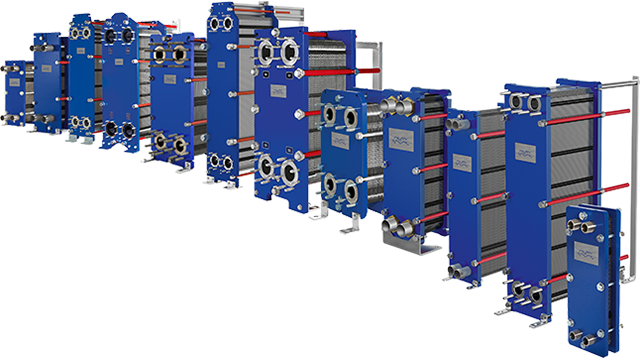
Energy supplier Taiyuan Heating Power Company has in fact started a partnership with Alfa Laval. The goal is to improve the Taiyuan Taigu Centralized Heating Supply Project, one of the largest central heating systems in the world. To improve the efficiency of the plant and reduce emissions, 90 large Alfa Laval plate heat exchangers will come to help. The choice fell on Alfa Laval because its heat exchangers can reduce carbon dioxide emissions of about 2.5 million tons by 4,000 tons, sulfur dioxide emissions, of 1,000 and 2,000 tons of oxychloride and dust respectively.
Another example comes from Saint Petersburg, Russia, where the tallest building in Europe, the Lakhta Center, uses 61 gasketed plate heat exchangers for the supply of hot and cold air, hot water and ventilation. Thanks to the high efficiency of heat exchange, these devices will minimize heat loss. The water consumption necessary for energy transfer will also be significantly lower. As a result, energy consumption for water pump operation will decrease.
The words of Alfa Laval
Further examples of urban and corporate environmental sustainability come also from Europe. The first in Hamburg, Germany, where eight Alfa Laval plate heat exchangers operate in an out-of-town copper processing plant. The residual energy captured by the four exchangers will reduce the energy consumption of the plant, while the other four exchangers will generate enough energy to heat 3,500 homes in the region.
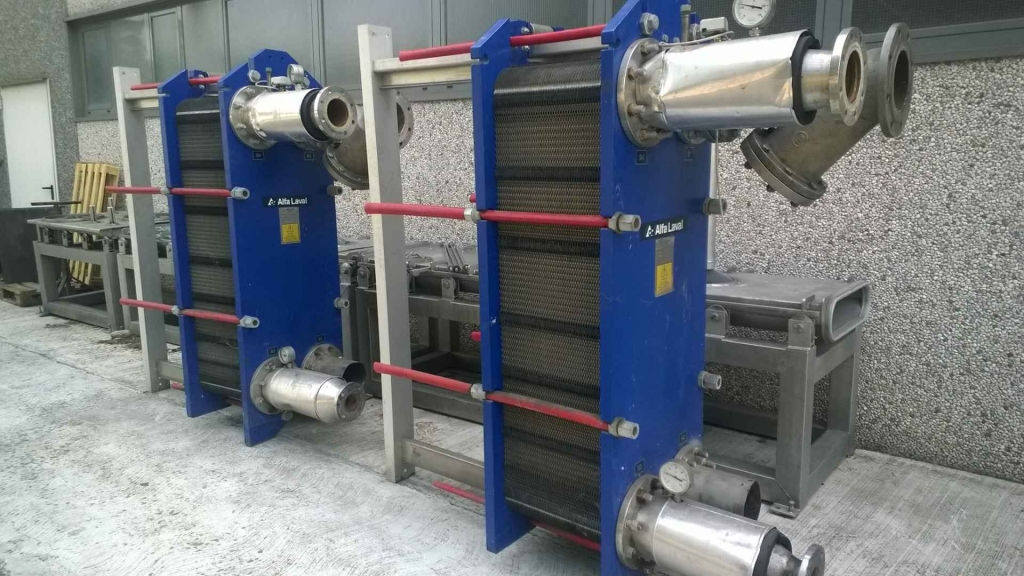

Julien Gennetier, president of Alfa Laval’s Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers Business Unit, underlined the global impact: «This result comes from the installation of a few units. It is easy to imagine the effects of the tens of thousands of exchangers we sell every year all over the world». The International Energy Agency estimates that in 2016 world energy consumption would have been 12% higher if no progress had been made in the field of energy efficiency.
The President of the Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers Business Unit also highlighted the winning combination between sustainability and the company vision: «You realize that you have to be relevant, not only in terms of sustainability, but also in terms of meeting needs of economic and social development […] Our technology is highly efficient and, since we are able to understand the processes of our customers, we can help them achieve their efficiency goals. All this makes our work truly rewarding».