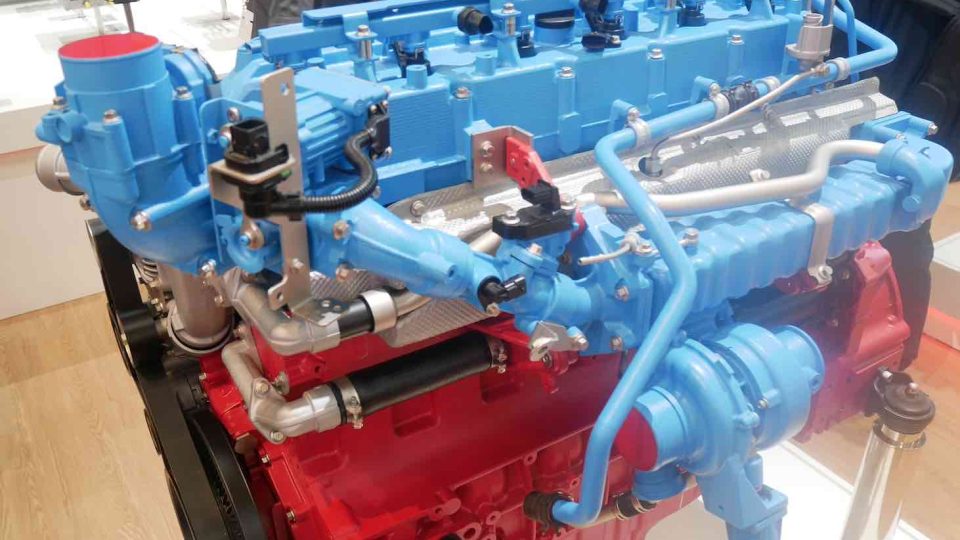
Indian OEMs and Volvo Penta: ready for upcoming regulations
Indian OEMs are receiving Volvo Penta’s attention Indian OEMs will need to comply with the stringent BS (CEV/Trem) IV emission regulations that will come into effect in October 2020. That’s why Volvo Penta, who’s already serving the market with its 5.1- and 7.7-liter engines, will satisfy this need through its Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology. […]
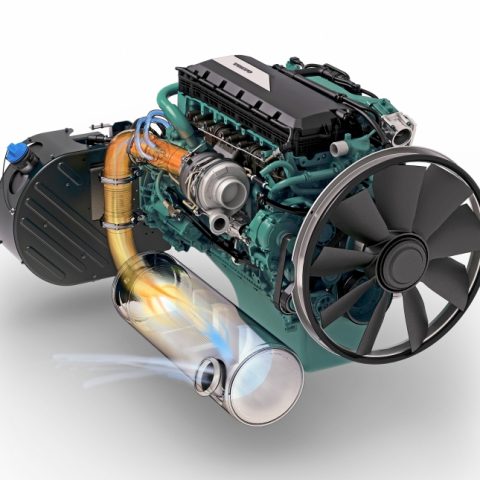
Indian OEMs are receiving Volvo Penta’s attention
Indian OEMs will need to comply with the stringent BS (CEV/Trem) IV emission regulations that will come into effect in October 2020. That’s why Volvo Penta, who’s already serving the market with its 5.1- and 7.7-liter engines, will satisfy this need through its Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology.
In 2011, Volvo Penta introduced the system for industrial off-road customers, further developing it in 2014. Today, Volvo Penta is still trying to answer environmental demands. In particular, with technologies at the service of BS (CEV/Trem) IV emission regulations. For OEMs, this means no re-generation, easy installation, continuous optimized fuel consumption and low operating costs.
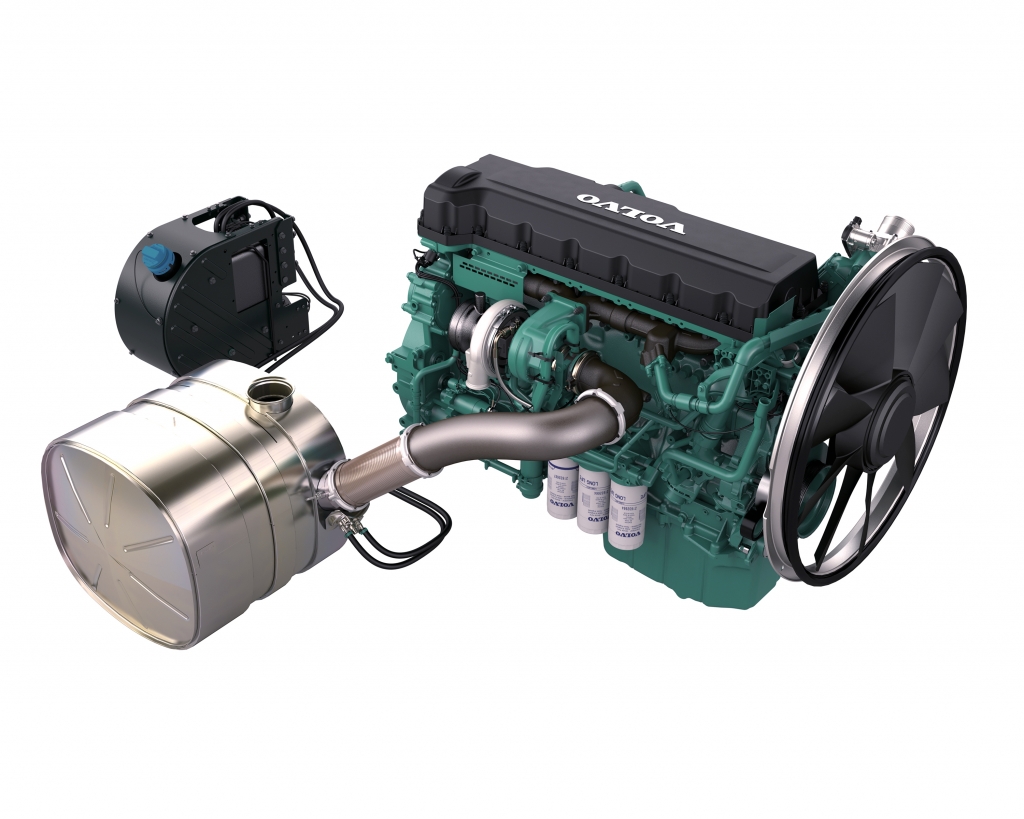

The current situation of the Indian market
For the Indian market, the current emission legislations applicable for off-road vehicles is BS (CEV) III from 2014, covering limited applications. Now BS (CEV/Trem) IV will be enforced from October 2020 and will cover most of the off-road applications.
In particular, with the introduction of BS (CEV/Trem) IV, all engine manufacturers will need to introduce aftertreatment systems for engines between 129 kW and 560 kW. This will put enormous demands on OEMs, forcing them to re-design their machines to install new engines and aftertreatment systems.
VOLVO PENTA IS ALSO READY FOR CHINA IV
Volvo Penta’s answer
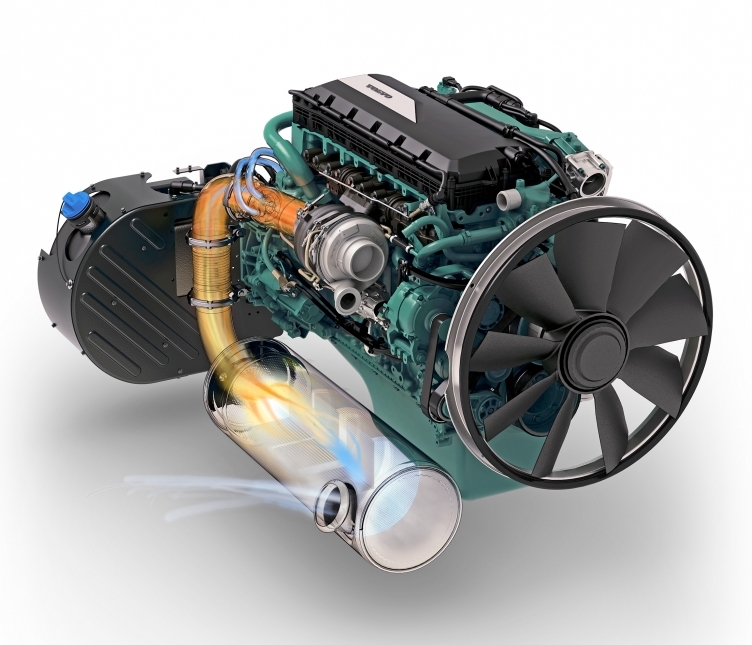
Volvo’s strategy is to keep these changes as simple as possible for Indian OEMs. SCR technology complies with BS (CEV/Trem) IV emission regulations without using a separate diesel particulate filter (DPF) or diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC).
The SCR system is based on high-efficiency combustion, which reduces the fuel consumption and results in low levels of particulate matter, but also in high levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx). The trick is that the exhaust NOx is then converted into nitrogen gas and water vapor.
Miron Thoms, Vice President and Head of Volvo Penta India, said: «We have extensive experience of SCR technology in the Volvo Group and we firmly believe that our BS (CEV/Trem) IV-compliant product range is industry-leading. We have been supplying BS (CEV/Trem) IV equivalent Stage IV/Tier4 Final engines globally since 2014 and have more than 200 OEM customers. From speaking to them, it’s clear our OEMs and operators are extremely pleased with competitive advantages of these engines in terms of no re-generation and easy installation, as well as low operating costs».
Volvo Penta has similar engine footprints for all emission standards. As a result, the OEMs already using Volvo Penta BS (CEV) III engines will have no trouble changing to a BS (CEV/Trem) IV model, as the SCR catalyst will simply just replace the current silencer. It will also allow for lesser regulated export markets to have no need of engine room redesign and be futureproof against the inevitable BS (CEV/Trem) V regulations.